Simple rng API and related functions. More...
Functions | |
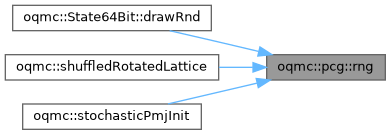
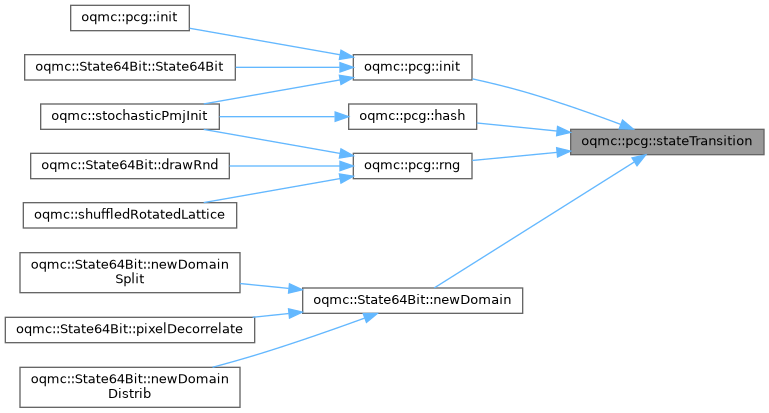
| constexpr std::uint32_t | oqmc::pcg::stateTransition (std::uint32_t state) |
| State transition function. | |
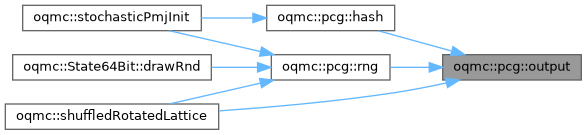
| constexpr std::uint32_t | oqmc::pcg::output (std::uint32_t state) |
| Output permutation function. | |
| constexpr std::uint32_t | oqmc::pcg::init () |
| Default initialise the PRNG state. | |
| constexpr std::uint32_t | oqmc::pcg::init (std::uint32_t seed) |
| Initialise the PRNG state using a seed value. | |
| constexpr std::uint32_t | oqmc::pcg::hash (std::uint32_t key) |
| Compute a hash value based on an input key. | |
| constexpr std::uint32_t | oqmc::pcg::rng (std::uint32_t &state) |
| Compute a random number from the PRNG sequence. | |
Detailed Description
This module outlines the RNG API which is used extensively as a building block in sampler implementations. PCG is used as both a classic sequential PRNG as-well-as a parallel hash function.
Here is a typical RNG example:
Here is a typical hash example:
Notice how one is statefull while the other is stateless. For best results use the RNG when possible. In both of these examples the rand values are integers. Use the oqmc::uintToFloat() function to convert the integers to floats.
When hashing, if you need to convert N inputs to 1 output, this can be done by nesting the hash function. However, nesting just the result from oqmc::pcg::stateTransition() is more optimal. If you do this make sure to call oqmc::pcg::output() prior to using the hash value.
This for example can be done to create the hash values for nodes and leaves in a tree. Which is especially fast if the intermediate values are re-used for subtrees. This is how domains are computed in OpenQMC.
Function Documentation
◆ stateTransition()
|
constexpr |
#include <oqmc/pcg.h>
Transition state using an LCG to increment the PRNG index along the sequence. Incrementing the input state can be used to select a new sequence stream. Note that you may want to use the higher level functionality below.
- Parameters
-
[in] state Internal state of the PRNG.
- Returns
- State after incrementation of index.
- Precondition
- State must have been initialised using an init function.
◆ output()
|
constexpr |
#include <oqmc/pcg.h>
Output permutation of the PRNG state, resulting in a usable random value with good statistical properties. This implements the three permutation operations used in PCG-RXS-M-32. Note you may want to use the higher level functionality below.
- Parameters
-
[in] state Internal state of the PRNG.
- Returns
- Output PRNG number from sequence.
- Precondition
- State must have been initialised using an init function.
◆ init() [1/2]
|
constexpr |
#include <oqmc/pcg.h>
If given no seed, initialise the PRNG state using a zero value. This must be done prior to passing the state to other functionality within this file.
- Returns
- Initialised internal state of the PRNG.
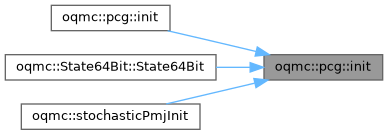
◆ init() [2/2]
|
constexpr |
#include <oqmc/pcg.h>
If given a seed, initialise the PRNG state using said seed value. This must be done prior to passing the state to other functionality within this file.
- Parameters
-
[in] seed Seed value for PRNG sequence.
- Returns
- Initialised internal state of the PRNG.
◆ hash()
|
constexpr |
#include <oqmc/pcg.h>
Given an input key, compute a random hash value. This can be used to initialise a system or to compute an array of random values in parallel.
- Parameters
-
[in] key Hash key value.
- Returns
- Output hash value.

◆ rng()
|
constexpr |
#include <oqmc/pcg.h>
Given a PRNG state, compute the next random number, and iterate the state for the next value in the sequence. Useful for generating high quality random numbers when computing them sequentially. The output number will be in the range of an unsigned 32 bit integer. For floating point numbers, this integer value needs to be converted into a floating point representation by the calling code.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] state State value of the PRNG. Will be mutated.
- Returns
- Output PRNG value from the sequence.
- Precondition
- State must have been initialised using an init function.